Formulas with polyatomic ions worksheet answers – Delving into the realm of formulas with polyatomic ions, this guide unveils the intricacies of these chemical entities, providing a comprehensive understanding through a journey of discovery and practical application. By unraveling the rules and nuances of formula writing, balancing equations, and delving into engaging worksheets, this guide empowers learners to navigate the complexities of polyatomic ions with confidence.
As we embark on this scientific expedition, we will explore the fundamental concepts of polyatomic ions, unraveling their unique characteristics and the significance of their formulas. Through a series of meticulously crafted examples and step-by-step explanations, we will master the art of formula writing, ensuring a solid foundation for further chemical endeavors.
Polyatomic Ions and Their Formulas
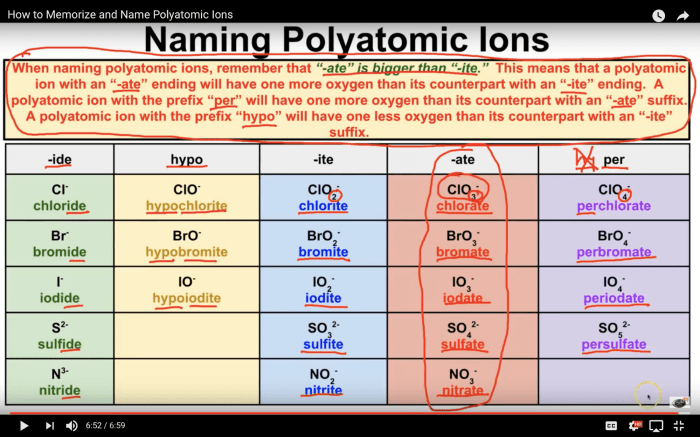
Polyatomic ions are charged chemical species composed of two or more atoms that remain together as a unit. They carry a net electric charge and behave as a single entity in chemical reactions. Common polyatomic ions include:
- Hydroxide (OH –)
- Carbonate (CO 32-)
- Nitrate (NO 3–)
- Sulfate (SO 42-)
- Phosphate (PO 43-)
Writing Formulas with Polyatomic Ions: Formulas With Polyatomic Ions Worksheet Answers
When writing formulas with polyatomic ions, the following rules apply:
- The net charge of the compound must be zero.
- The metal ion and polyatomic ion must combine in a ratio that balances their charges.
For example, to write the formula for sodium carbonate, we know that sodium is a metal with a charge of +1 and carbonate is a polyatomic ion with a charge of -2. To balance these charges, we need two sodium ions for every carbonate ion, resulting in the formula Na 2CO 3.
Balancing Chemical Equations with Polyatomic Ions
When balancing chemical equations involving polyatomic ions, the following steps can be followed:
- Balance the elements other than the polyatomic ion first.
- Balance the polyatomic ion by adjusting the coefficients of the compounds that contain it.
- Check that the equation is balanced by verifying that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides.
For example, to balance the equation:
Fe + 2HCl → FeCl 2+ H 2
we would first balance the Fe and Cl atoms by adding a coefficient of 2 to FeCl 2:
Fe + 2HCl → 2FeCl 2+ H 2
Then, we would balance the H atoms by adding a coefficient of 2 to H 2:
Fe + 2HCl → 2FeCl 2+ 2H 2
General Inquiries
What are polyatomic ions?
Polyatomic ions are charged species composed of two or more atoms covalently bonded together, carrying a net electrical charge.
How do I write formulas for compounds containing polyatomic ions?
To write formulas for compounds containing polyatomic ions, you must consider the charges of the ions involved and ensure that the overall charge of the compound is neutral.
How do I balance chemical equations involving polyatomic ions?
Balancing chemical equations involving polyatomic ions requires careful consideration of the charges of the ions and the coefficients of the reactants and products.