Left lateral decubitus x ray – In the realm of medical imaging, the left lateral decubitus x-ray stands tall, offering a unique perspective into the human body. This imaging technique plays a crucial role in diagnosing and managing a wide range of conditions, empowering healthcare professionals with valuable insights.
By positioning the patient on their left side, this x-ray allows for optimal visualization of specific anatomical structures, providing a wealth of information for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
Left Lateral Decubitus Position
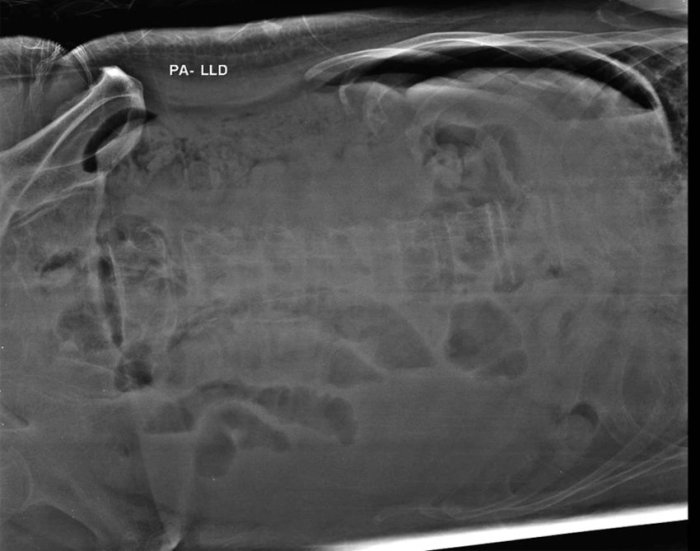
The left lateral decubitus position is a diagnostic imaging technique used to visualize the abdominal and pelvic organs. It involves positioning the patient on their left side with their right side facing up.
Purpose, Left lateral decubitus x ray
The left lateral decubitus position is primarily used to:
- Evaluate the size, shape, and position of the abdominal and pelvic organs.
- Detect fluid collections or masses within the abdomen or pelvis.
- Assess the patency of the gastrointestinal tract.
Proper Positioning
To properly position the patient in the left lateral decubitus position:
- Instruct the patient to lie on their left side with their right side facing up.
- Flex the patient’s right knee and hip to bring their right leg up towards their chest.
- Support the patient’s right arm behind their head.
- Ensure that the patient’s left arm is extended along their side.
Benefits
The left lateral decubitus position offers several benefits, including:
- Improved visualization of the abdominal and pelvic organs due to the removal of overlying structures.
- Reduced radiation exposure to the patient compared to other imaging techniques.
- Increased patient comfort and reduced anxiety as the patient is not lying on their back.
Indications for Left Lateral Decubitus X-Ray
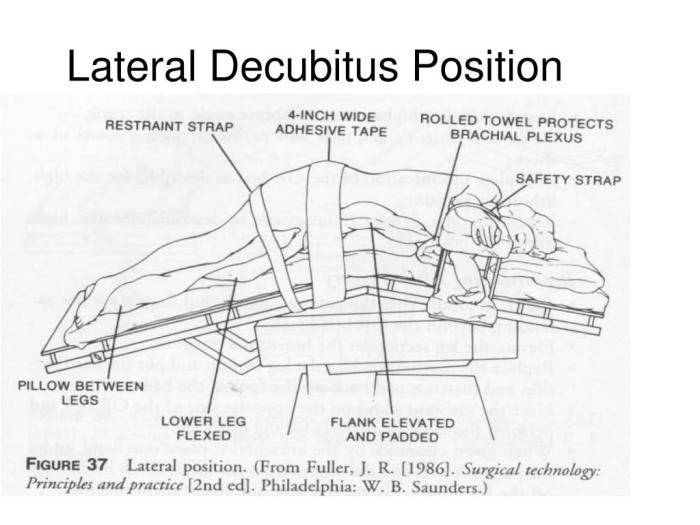
The left lateral decubitus position is commonly used in diagnostic radiology to visualize specific anatomical structures and detect certain medical conditions. Here are the primary indications for ordering a left lateral decubitus x-ray:
- Evaluation of pleural effusions:The left lateral decubitus position allows for the detection and estimation of pleural effusions, which are collections of fluid in the pleural space. When a patient is positioned on their left side, any free-flowing pleural fluid will gravitate to the right side of the chest, making it more visible on an x-ray.
- Assessment of lung consolidation:The left lateral decubitus position can help identify and assess lung consolidation, which is a condition characterized by the filling of alveoli with fluid or inflammatory cells. By positioning the patient on their left side, any areas of consolidation in the right lung will become more prominent and easier to detect on an x-ray.
- Diagnosis of pneumothorax:A left lateral decubitus x-ray can be used to diagnose pneumothorax, a condition in which air is present in the pleural space. When a patient is positioned on their left side, any air in the pleural space will rise to the apex of the right lung, making it visible on an x-ray.
- Evaluation of mediastinal masses:The left lateral decubitus position can help visualize and evaluate mediastinal masses, which are abnormal growths or collections of fluid in the mediastinum. By positioning the patient on their left side, the heart and other mediastinal structures will shift slightly, allowing for better visualization of any masses.
Anatomy Visualized on Left Lateral Decubitus X-Ray
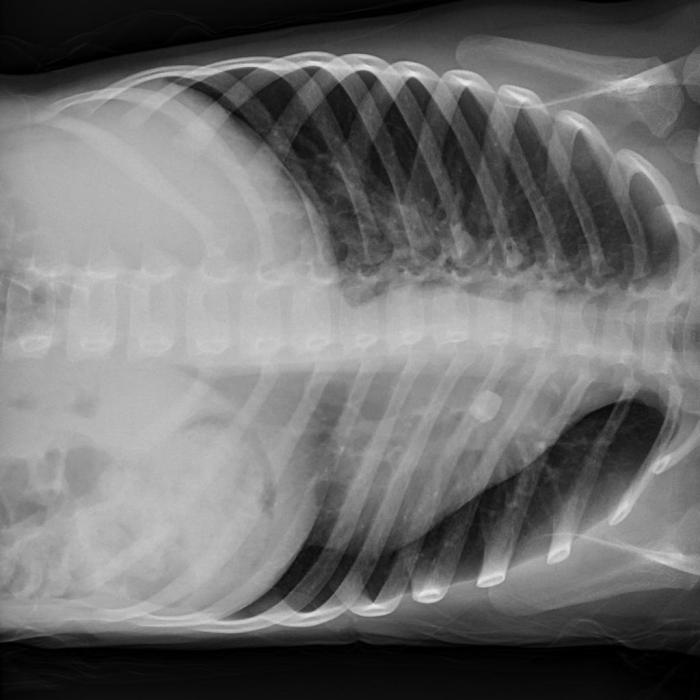
The left lateral decubitus position is particularly useful for visualizing specific anatomical structures within the chest and abdomen. This position allows for optimal visualization due to the shifting of organs and fluids within the body.
Structures Visualized
- Lungs:The left lateral decubitus position allows for better visualization of the posterior and lateral aspects of the lungs, including the lingula and lower lobes. This is particularly useful for detecting abnormalities such as infiltrates, consolidations, and pleural effusions.
- Heart:The left lateral decubitus position shifts the heart anteriorly, making it easier to visualize the left atrium and ventricle. This can be helpful in evaluating cardiac size and function, as well as detecting pericardial effusions.
- Mediastinum:The left lateral decubitus position can help differentiate between mediastinal masses and aortic aneurysms. The mass will shift with the mediastinum, while the aneurysm will remain stationary.
- Abdomen:The left lateral decubitus position can be used to detect free fluid in the abdomen, such as ascites. The fluid will collect in the dependent portion of the abdomen, which is the right side when the patient is in the left lateral decubitus position.
Comparison to Other Imaging Modalities: Left Lateral Decubitus X Ray
The left lateral decubitus x-ray is often compared to other imaging modalities, such as supine or upright x-rays, to determine the most appropriate technique for specific imaging purposes. Each modality has its own advantages and disadvantages, making it important to understand the differences between them.
Advantages of Left Lateral Decubitus X-Ray
- Improved visualization of fluid collections: The left lateral decubitus position allows fluid to accumulate in the dependent portion of the abdomen, making it easier to detect small amounts of fluid that may not be visible on supine or upright x-rays.
- Detection of free air: Air rises to the highest point in the abdomen, and the left lateral decubitus position allows for better visualization of free air under the diaphragm, which can be indicative of a perforated viscus.
- Assessment of bowel distension: The left lateral decubitus position can help to differentiate between distended loops of small bowel and large bowel, which can be important in diagnosing conditions such as small bowel obstruction.
Disadvantages of Left Lateral Decubitus X-Ray
- Limited visualization of the lungs: The left lateral decubitus position can make it difficult to visualize the lungs, as the heart and mediastinum are superimposed on the lung fields.
- Patient discomfort: The left lateral decubitus position can be uncomfortable for patients, especially those with respiratory or cardiovascular problems.
- Increased radiation exposure: The left lateral decubitus position requires a higher radiation dose than supine or upright x-rays, as the x-ray beam must penetrate more tissue.
When to Use Left Lateral Decubitus X-Ray
The left lateral decubitus x-ray is most commonly used to evaluate the abdomen for fluid collections, free air, or bowel distension. It is also useful for assessing the position of the diaphragm and for detecting pneumothorax.
Clinical Applications
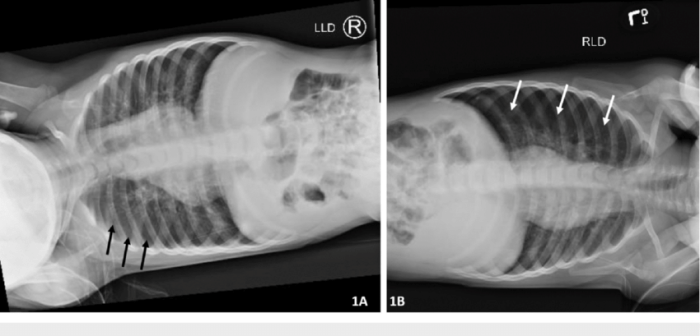
The left lateral decubitus X-ray is a versatile imaging technique that provides valuable information in various clinical scenarios. By utilizing the left lateral decubitus position, clinicians can visualize anatomical structures and assess their function, contributing to the diagnosis and management of a wide range of conditions.
The left lateral decubitus position is particularly useful for evaluating conditions affecting the lungs, pleura, and mediastinum. In cases of pleural effusion or pneumothorax, the left lateral decubitus position allows for the accumulation of fluid or air in the dependent portion of the pleural space, making it more visible on the X-ray.
Evaluation of Pleural Effusions
In patients with suspected pleural effusions, the left lateral decubitus X-ray can help confirm the presence and extent of fluid collection. The fluid will gravitate to the dependent portion of the pleural space, typically seen as an opacity in the left lower lung field.
Left lateral decubitus x ray, a diagnostic imaging technique, provides valuable insights into a patient’s anatomy. Similarly, in the realm of music theory, the e minor triad bass clef notation serves as a fundamental building block for constructing harmonies and melodies.
Returning to left lateral decubitus x ray, this technique continues to play a crucial role in medical diagnosis, aiding healthcare professionals in making informed decisions.
The X-ray can also provide information about the underlying cause of the effusion, such as heart failure, liver disease, or infection.
Assessment of Pneumothorax
The left lateral decubitus X-ray is essential in diagnosing and assessing the severity of a pneumothorax. Air in the pleural space will rise to the highest point, which is the right apex in the left lateral decubitus position. The presence of a pneumothorax is indicated by a radiolucent (black) area beneath the right clavicle.
The size of the pneumothorax can be estimated by measuring the width of the air-filled space.
Image Interpretation
Interpreting left lateral decubitus x-rays involves careful evaluation of the fluid levels, gas patterns, and organ positioning within the abdomen.
Radiologists assess these images to identify any abnormalities that may indicate underlying medical conditions.
Key Findings
- Fluid levels:Horizontal lines within the abdomen that indicate the presence of fluid.
- Gas patterns:Collections of gas within the intestines that can help identify bowel obstruction or perforation.
- Organ positioning:The position and shape of organs such as the liver, stomach, and intestines can provide clues about underlying conditions.
Tips for Identifying Normal and Abnormal Findings
- Normal findings:
- A single fluid level in the stomach.
- Gas-filled loops of intestine in the left upper quadrant.
- The liver located in the right upper quadrant.
- Abnormal findings:
- Multiple fluid levels.
- Gas patterns that suggest bowel obstruction.
- Displacement of organs from their normal positions.
Detailed FAQs
What is the purpose of a left lateral decubitus x-ray?
The left lateral decubitus x-ray is used to visualize specific anatomical structures, such as the heart, lungs, and abdomen, from a unique perspective.
When is a left lateral decubitus x-ray typically ordered?
A left lateral decubitus x-ray may be ordered to diagnose or monitor conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, or pleural effusion.
How does the left lateral decubitus position improve visualization?
The left lateral decubitus position allows for better visualization of certain anatomical structures by shifting overlying structures out of the way.